Grasshopper Workshop Agenda and Exercises
 | Grasshopper Wiki Pages |
| Robert McNeel & Associates |
Summary: Opensource Community page to help support instructors who are teaching the Grasshopper plug-in
The most up-to-date information is on the Grasshopper Group site. This page may give everyone a place to contribute and learn on teaching the Grasshopper.
Instructional goal or outcome
This workshop will give students a functional understanding of Grasshopper, so that they can build on this understanding for more advanced projects of their own.
- A basic understanding of the Grasshopper interface
- Troubleshoot definition problems and solutions
- Know the main component types
- Be able to join, and manage connections
- Use Expressions for both calculation and boolean creation
- Understand Data Matching
- Understand list management within Grasshopper
- Have a basic understanding of Grasshopper components
- Experience creating a few of their own definitions
General interface tricks
Detail explanation on the interface
Definitions: Shift.ghx
Document: Interface Explained.pdf
Interface overview
- The screen
- Navigation around a definition
- Panning
- Zooming
- Resetting the view
- Searching for a component - Double-click on screen
- Saving definitions
- The GHX file
- The Rhino file
- Other files
- GH file
- WRM files
- Opening and editing your first definition
- Looking at the flow from left to right
- Understanding how to hover over inputs and outputs to see how components are working
Connecting components
- Creating connections
- Deleting connections
- Multiple connections
- Component search - Double-click on background
Debugging information
- Component colors
- Debugging Window
- Input and output mouse hover
Commenting definitions
Definitions: Simple Math.ghx
- Post-its
- Using Post-it to note definitions
- Using post-it to document input or output
- Drawing Curves
- Free-form
- Rectangles
Components
The core of Grasshopper is the component. Detailed explanation of components.
Document: Objects Explained.pdf
Definition: Need to build up a definition that can be used to create these objects. Perhaps a circle based definition.
Parameter component type
Parameters are a special type of component. Many times you might start with a definition. Parameters are singular entities that reference or contain data. In traditional programing they are most similar to declared variables. Typically parameters are your starting and controlling values in the definition. There are three types of parameters: Primitive, U\I, and Geometry.
- Primitive component
- Holding a value
- As a translator
Definition: Simple parameters - Build a definition with floats and integers. See the results. Start with the multi component. Set a float to each input. See the result. Change one of the inputs. See results. Then run one of the floats through a int param to round it off.
- U\I components
- The slider
Definition: Simple parameters - Build a definition with points and circles see the results.
- Geometry parameter components
- Picking from a Rhino object
- Implicit components
Definition: Simple parameters - Build a definition with points and circles. See the results. Start with the C,N,R circle component. Add a point param. set to C. Then set a Float param to R. See the result. Introduce that a param can handle multiple objects. Right-click on point. Then select multiple select. Pick multiple points. You should see many circles. If you want them to draw multiple Rhino points, then select them all with the Point param. You can now move the points around.
- Parameter component colors
- Orange - empty
- Grey - with data
- Hatched - not previewing
Definition: Simple parameters
Component
- Compared to a primitive, component is more involved since it contains input and output parameters, expressions, data matching behavior.
- A standard component takes information from its left and processes the data out to the right.
- Component color\status.
- Orange - not enough inputs.
- Grey - functioning fine with data
- Red - a component which contains at least one error. The error can come either from the component itself or from one of its input/output parameters.
- Hatched - not previewing
- Volatile vs Persistant Data Management in components
- Data handling - understanding how to manipulate lists and data is critical to understanding Grasshopper
- Handling a list of inputs
- Matching a list of data
- Built-in data matching - http://grasshopper.rhino3d.com/2008/06/description-of-data-stream-matching.html
- Short list
- Long list
- Cross reference
- Connecting
- One or multiple connectors to inputs or outputs.
- Disconnecting with a right-click
- Visible component preview
- Preview Off-On
- Rendering of a component that is not previewing (Hatch)
- Rhino Preview Object Colors
- Blue feedback geometry means you are currently picking it with the mouse.
- Green geometry in the viewport belongs to a component which is currently selected.
- Red geometry in the viewport belongs to a component which is currently unselected.
- Point geometry is drawn as a cross rather than a rectangle to distinguish it from Rhino point objects.
Scalar component types
These are for primary mathematical functions.
- Expressions
- Operators
- Polynomials
- Trigonometry
- Custom Math Functions
Definition: Simple Math
Interval vs Series vs Range
- Intervals - A range of all numbers between a low and high number.
- Range - A list of evenly spaced numbers between a low and a high value
- Series - A list of discrete numbers
Definitions: Simple Math.ghx
Expressions
- Formula component
- Expressions within components
- Expression editor
Definitions: Simple Math.ghx
- Uses of expressions
- Unit Conversion - at the end of a slider
- 0 indexing of a list
Vectors and planes
- Vector as a direction
- Plane/Frame as a construction plane
Make a building
Create shell
- Create a base point
- Create and elipse component with sliders for width and height
Thicken floors
Elevator shaft
Booleans and expressions
- True\False Booleans
- Creating Booleans
- Component
- Expression
- Booleans in list culling
- Booleans and logic gates
Definition: Create a cloud of points and a curve. Use and Expression to turn off points that are further from the curve than a specific value.
Definition: Change to include a point on the curve. Then using Boolean gates, set a points that are within the curve and the point.
Sorting
- Sorting on list with another
- Numbering the order with 3D text
Definition: Continuing with the Booleans definition above, sort the points based on their distance from an atractor point on the curve. You can use the Tag object to number the points to show their sort order. As an extension, you can draw a circle from the atractor point to the 6th sorted point.
Advanced topics
Clusters
- Using Clusters
- Cluster tips and tricks
Script component
Inside a Grasshopper workshop only the most basic of scripting concepts can be presented. A script component can be used to manupulate data in a way that existing components cannot. You can also create geometry with script components. Grasshopper can handle both C# and VB.NET coded components. It is important to note here that Grasshopper does not support RhinoScript directly. The VB.NET component is the best to use if you are coming from the RhinoScript language. There are quite a few differences between RhinoScript and VB.NET, so it will take time to make the transition. This course covers only VB.NET.
Definition: http://en.wiki.mcneel.com/content/upload/files/points_examples.zip
General setup
When you drag and drop a VB.NET component you get a base VB.NET code component. By default it has two inputs (x & y) and one output (A). It also has a message output (out) to see error messages.
To edit the component, just double-click on the component. You will get a basic code editor.
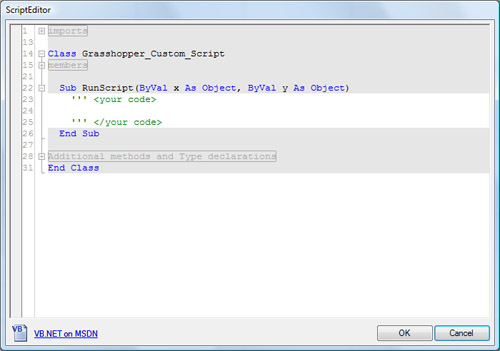 You cannot edit the gray areas. The white background area is where you add your own code.
You cannot edit the gray areas. The white background area is where you add your own code.
Simple scripting flow: Seeing a script as a loop
Each time a piece of data flows into an input, the script you type runs. In the most simple case a script can be used as a math function. This could also be done with a math function component, but it is used here as a simple example of scripting.
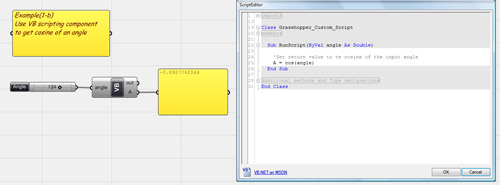
Sub RhinoScript(ByVal angle As Object)
' Set return value to the cosine of the input angle A = Cos(angle)
End Sub
Here you can see that every time the slider is changed, the code runs in the VB.NET component. The last line of the code states A =. This is the place that the output value is assigned the A output on the component.
Also, there is a line the starts with a '. This make the line a comment. It is ignored by the code when it runs, but is used to comment the code to help us understand what is going on.
Variables
Perhaps the most important part of VB.NET programming is understanding variables and datatypes. Variables are containers of the information. The value of data in a variable can change within your code. It is through variables that you store, edit, and retrieve information. There are a few basics to understand about variables.
Variables are containers of information. And, like any real container, depending on what you intend to store in the container you may select from different containers sizes and styles. It is important to know the type of data you intend to contain in the variable. Each piece of data you intend to work with has a different size and therefore requires a different size container.
When you create a new Variable in VB.NET you must declare what type (size) the container needs to be in order to hold the information you have.
- Input Data
- Basic Input
- Location of input variables - At the top of the code
- Type - Object unless using the Type Hint on the input itself
- Adding - Adding more inputs
- Subtracting - Subtracting inputs
- Renaming - Right-click to rename input names
- Declaring variables
- Basic variable types - Value types: Boolean, Char, Integer, Long, ULong, Double, etc.
This line declares a simple Integer container with the name is i.
Dim i As Int32
* Reference Variable types String, Object.
Dim name As String = "Arthur"
Dim name As Object = "Arthur"
- Object Variable Types - opennurbs objects (ON3dPoint, ONCircle etc) or any object of a user defined class. These containers require a new statement when they are being created to invoke the constructor of the object and initialize object member variables. Otherwise it is initialized to null:
Dim pt As New On3dPoint 'Initialized to (0,0,0) by the default constructor
Dim pt As New On3dPoint(1.0, 2.0, 3.0) 'User initialize point pt.x = 10 'Changing value of a member variable
- Outputting data
- Method - Use “A =”
Sub RhinoScript(ByVal point As ON3dPoint, ByVal dis As Object)
point.x = point.x + (2 * dis) point.y = point.y + (dis * cos(dis)) point.z = point.z
A = point
End Sub * Types * Multiple Outputs - Sometimes you want to output more than one variable each time the loop goes through. For instance if you have two input lists you would like to combine. In this example you have two lists of 5 items each. So you are going to go through your code 5 times. The problem is that you want to output one list with 10 items. So each time through the code, you will want to output two items. To do this you need to use a List object. Dim points As New List(Of On3dPoint)
To add a new member of a list use the .add method
points.Add(new_pt)
Here is a full sample:
Sub RunScript(ByVal x As Object, ByVal y As Object) Dim Sorted As New List(Of Object) Sorted.Add(x) Sorted.Add(y) A = Sorted End Sub
- Looping - Standard VB.NET looping and flow control can be used.
- If..Then
- For…Next
Definition - opennurbs is the way we create and access geometry items in Rhino.NET. You can create points, lines, and many other geometry types.
- Using opennurbs objects.
- If you find that you have students that are familiar with RhinoScript, you may want to present some of the differences between RhinoScript and Grasshopper's VB.NET code.
Specialty components
- Graph component
- Curve distribution component
- Fibonacci sequence component
- Jitter component
- The Post-its as component
- Post-It notes can write their contents to text files