Zoo Troubleshooting
Product: Zoo 4.0
Summary: Tips for solving problems related to the Zoo Workgroup License Manager.
The Zoo uses a simple, protocol-independent messaging technology called Mailslots to communicate with Rhino. Microsoft networks use mailslots messages in a variety of areas, including domain logon service. Mailslot messaging works on all modern Microsoft operating systems. Mailslot messaging works on both Workgroup networks and on Domain networks.
For configuring the Zoo, there really is nothing to do. As long as all machines involved belong to the same Windows Domain or Workgroup and are installed on the same subnet, then the Zoo should be able to allocate licenses upon request. Keep a couple of things in mind when working with the Zoo:
- Make sure you are running the latest version of the Zoo.
- Make sure you are logged in as the Administrator or as a member of the Administrators group when running the Zoo console application.
- Make sure you are running the latest service release of Rhino and other Zoo-supporting plug-ins, such as Brazil, Bongo, Flamingo and Penguin.
Application notes
- The Zoo will run on Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2000, 2003 and 2008 systems.
- The Zoo requires that the Microsoft C++ 2005 SP1 Redistributable Package (x86) be installed on the system.
- The Zoo will not work with Rhino 2.0 or 3.0 Educational or Educational Lab licenses (CD-Keys).
- The Zoo will not work with Rhino 2.0 or 3.0 running on Asian versions of Windows.
- Not all products are capable of acquiring licenses across a routed network. See the Zoo Product Compatibility page for a list of what works and what does not.
- Log in as the Administrator or as a member of the Administrator's group when running the Zoo console application.
Networking notes
- All systems must belong to the same Windows Domain or Workgroup.
- Make sure the network connection that you are using has the Client for Microsoft Networks installed and enabled. Otherwise, you will get Failed to write to client mailslot errors written to the Zoo log file.
- If you using TCP/IP, make sure to Enable NetBIOS over TCP/IP in the advanced TCP/IP options. Otherwise, you will get Failed to write to client mailslot errors written to the Zoo log file.
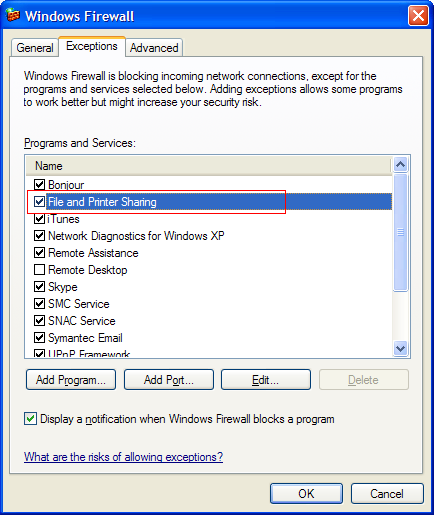
- If the computer running either Rhino or the Zoo is using a firewall, be sure that the following ports are open:
- UDP Ports 137 and 138
- TCP Port 139
- Note, these are ports that Windows uses for NetBIOS communications. If you are using the built-in Windows Firewall, enable File and Printer Sharing as an allowed exception.
- If you have not configured your Rhino systems for either DNS or Registry Key lookup, then all Rhino workstations and the system running the Zoo must be installed on the same network subnet. This is because both Rhino and the Zoo will broadcast messages. Broadcast mailslot messages will not cross network routers and some switches. Also, wireless routers will not forward broadcast messages.
Ensure name resolution works between Zoo and Client
The nbtstat is designed to help troubleshoot NetBIOS name resolution problems. When a network is functioning normally, NetBIOS over TCP/IP resolves NetBIOS names to IP addresses. It does this through several options for NetBIOS name resolution, including local cache lookup, WINS server query, broadcast, LMHOSTS lookup, Hosts lookup, and DNS server query.
To test name resolution using nbtstat:
- On the Zoo server, open a Command Prompt.
- Type nbtstat -a <ClientComputerName>.
- One of the network adapters should resolve the client computer name.
- On the Client computer, open a Command Prompt.
- Type nbtstat -a <ZooServerName>.
- One of the network adapters should resolve the Zoo computer name.
If nbtstat fails to return information for either the Zoo or the Client, then the Zoo will not work with this network configuration. It is beyond the scope of this document and McNeel Support to help you ensure that your network supports proper NetBIOS name resolution.
Ensure connectivity works between Zoo and Client
The net view command displays a list of domains, computers, or resources shared by the specified computer. Used without parameters, net view displays a list of computers in your current domain.
To test connectivity by using the net view command:
- On the Zoo server, open a Command Prompt.
- Type net view \\<ClientComputerName>.
- On the Client computer, open a Command Prompt.
- Type net view \\<ZooServerName>.
The net view command lists the file and print shares by establishing a temporary connection.
- If there are no file or print shares on the specified computer, the net view command displays a There are no entries in the list message.
- If the net view command fails with a System error 53 has occurred message, verify that the specified computer name is correct, that the computer is operational, and that all the gateways (routers) between this computer and the computer are operational.
- If the net view command fails with a System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. message, verify that you are logged in with an account that has permission to view the shares on the remote computer.
To further troubleshoot this connectivity problem, do the following:
- Use the net view command and the IP address of the computer, as follows: net view \\<IPAddress>.
- If the net view command succeeds, then the specified computer name is being resolved to the wrong IP address.
- If the net view command fails with a System error 53 has occurred message, the remote computer might not be running the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks service.
Zoo notes
- The Zoo can maintain a log file, ZOO.LOG, of conversations with Rhino clients. The log file can be useful in diagnosing some communication problems. If you do not see a log file in the same folder as ZOO.EXE, then you can turn on logging by selecting Tools→Options from within the Zoo application. Check the log file, using NOTEPAD.EXE, to see if Rhino messages are making it to the Zoo, and that the Zoo is responding to these messages.
Zoo bonus tools
If you are using the Zoo on routed networks and Rhino is unable to find the Zoo, then the Zoo lookup, either Registry Key or DNS, may not be configured correctly. You might see if one of the Zoo Bonus Tools can assist in resolving the problem. The Zoo Bonus Tools include the following utilities:
- SetZooServer.exe - Assists in configuring workstations for Registry Key lookup.
- ZooDnsResolver.exe - Assists in testing the DNS Lookup feature.