Zoo - Diagnostics Utility for Windows
Product: Zoo
Summary: Discusses the Zoo Diagnostics utility for Windows
Need Mac? Go here.
The Zoo Diagnostics utility runs on a Rhino for Windows workstation. The utility provides these useful tools:
- Provides several useful network diagnostics to troubleshoot connectivity issues between Rhino for Windows workstations and Zoo servers.
- Lets you view and change the name of the LAN Zoo server used by Rhino workstations. The LAN Zoo server name is stored in the Windows Registry.
Download
Pick to Download Zoo Diagnostics
Diagnostics
The Zoo Diagnostics utility provides these useful network tests:
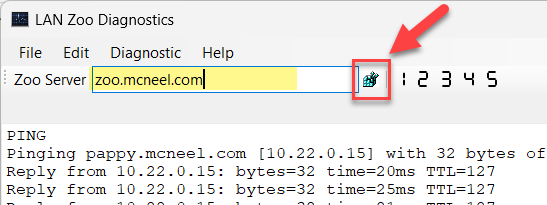
1. Ping: The Ping (PING) diagnostics utility is the primary TCP/IP tool used to troubleshoot connectivity, reachability, and name resolution. Ping verifies IP-level connectivity to another TCP/IP computer by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages. Receipts of corresponding Echo Reply messages are displayed, along with round-trip times.
Note: The Windows firewall default settings block the ICMP echo requests used for ping command. To enable ICMP echo on Windows, go to Control Panel → Windows Firewall → Advanced settings → Inbound Rules and enable File and Printer Sharing (Echo Request - ICMPv4-In) in the active security profile.
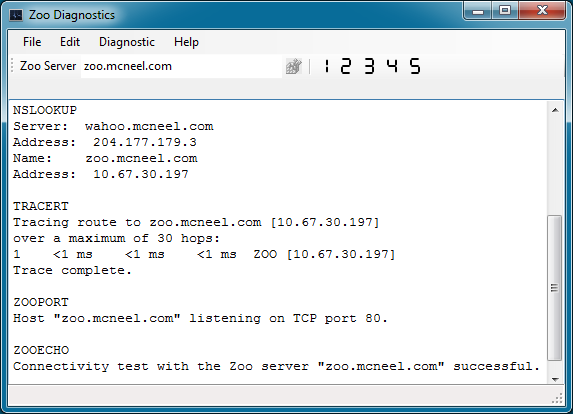
2. Nslookup: The DNS Lookup (NSLOOKUP) diagnostic utility displays information that you can use to diagnose Domain Name System (DNS) infrastructure.
3. Trace Route: The Trace Route (TRACERT) diagnostic utility determines the route taken to a destination by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets with varying IP Time-To-Live (TTL) values to the destination. Each router along the path is required to decrement the TTL on a packet by at least 1 before forwarding it, so the TTL is effectively a hop count. When the TTL on a packet reaches 0, the router should send an ICMP Time Exceeded message back to the source computer.
4. Zoo Port Check: The Zoo Port Check (ZOOPORT) diagnostic utility verifies that a Zoo service is listening on TCP Port 80 on a server or workstation.
If this test fails, then make sure the Zoo server service is running. You can do this by using either ZooAdmin.Wpf.exe or the Services applet in Control Panel. Also, make sure TCP Port 80 is open on any firewall software, for both incoming and outgoing traffic, running on the Zoo system.
Also look at the results above from Trace Route. If you see multiple subnets in the list, you will likely need to change the firewall rules on your LAN Zoo server to allow connections from multiple subnets. See Open TCP Port 80 in Windows Firewall Using Netsh for details.
5. Zoo Connectivity: The Zoo Connectivity (ZOOECHO) diagnostic utility verifies that the Zoo service is running on a server or workstation.
If this test fails and all other tests succeed, then make sure the Zoo server service is running. You can do this by using either ZooAdmin.Wpf.exe or the Services applet in Control Panel. Also, make sure TCP Port 80 is open on any firewall software, for both incoming and outgoing traffic, running on the Zoo system.
This test can fail if the client and server are on different subnets. By default, the Zoo installer opens the Windows Firewall to the Zoo service on port 80 for the local subnet only. You will need to change the firewall rule “Scope” property to allow all other subnets that need access.
This test can also fail if your system is configured to access the Internet by using a Proxy Server. In this case, the test never reaches the Zoo server. If you are using a Proxy Server, make sure you allow access to local addresses. See Using Zoo with a Proxy Server for details.
6. Set Your Zoo Server Name
Type your Zoo Server name or IP. (This is our DNS name. You need to provide your own.)
Pick the button to save your Zoo server name or IP to the Registry.
The Zoo server name is written to
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\McNeel\Rhinoceros\x\License Manager where x is the version of Rhino.